-
[JPA] DB IDENTITY 전략일 때, 영속성 컨텍스트legacy/JPA 2023. 9. 4. 11:06

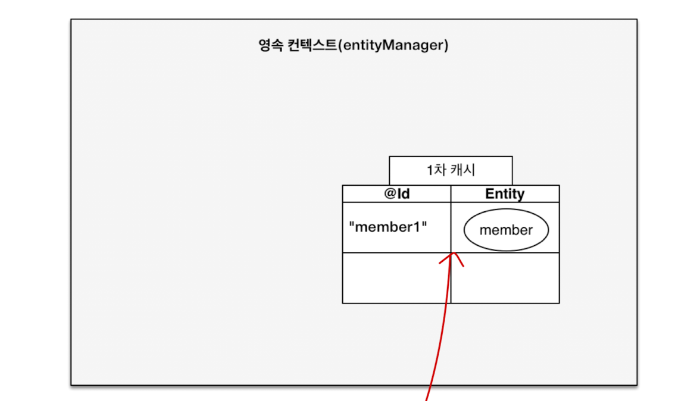
JPA의 경우에 EntityManager를 통해 persist를 하면 해당 객체는 영속 상태가 된다. DB에 저장된 상태가 아닌 1차 캐시에 ID-Entity 형태로 JPA에 의해 관리가 된다. 또한 Member 엔티티를 DB에 저장하기 위한 Insert 쿼리문이 DB로 날라가지 않고 쓰기 지연 저장소에 보관된다.
아래는 Member 엔티티를 persist 하였을 때, 1차 캐시에 저장되어 JPA에 의해 관리 중인 상태이다.
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello"); EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager(); EntityTransaction transaction = em.getTransaction(); transaction.begin(); try { Member member = new Member(); member.setUsername("hope"); em.persist(member); System.out.println("persist"); System.out.println("commit"); transaction.commit(); } catch(Exception ex) { transaction.rollback(); } finally { em.close(); emf.close(); }엔티티를 persist()했을 때 Insert 쿼리문이 나가지 않음을 알 수 있다. persist() 시점에는 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소에 쿼리문을 보관한다. 이후에 commit을 할때 쓰기 지연 SQL 저장소에 보관된 쿼리문이 DB로 날라가게 된다.
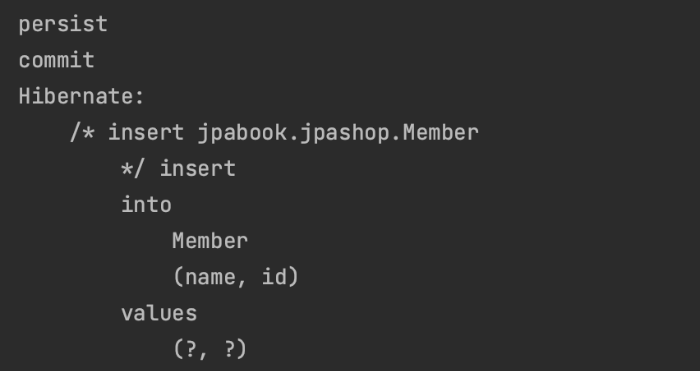
그러나 DB의 PK가 IDENTITY 전략에 의해 자동으로 생성된다면 말이 달라진다.
IDENTITY 전략인 경우에는 Entity를 persist함과 동시에 DB에 INSERT 쿼리를 날린다. 즉, 1차 캐시에 저장됨과 동시에 쓰기 지연 저장소에 SQL을 저장하지 않고 바로 DB로 쿼리문을 날리게 된다.
EntityManagerFactory emf = Persistence.createEntityManagerFactory("hello"); EntityManager em = emf.createEntityManager(); EntityTransaction transaction = em.getTransaction(); transaction.begin(); try { Member member = new Member(); member.setUsername("hope"); em.persist(member); // IDENTITY -> 영속성 컨텍스트 1차 캐시에 저장됨과 동시에 DB에 쿼리 날린다. System.out.println("persist"); System.out.println("commit"); transaction.commit(); } catch(Exception ex) { transaction.rollback(); } finally { em.close(); emf.close(); }em.persist()를 함과 동시에 Insert 쿼리문이 나가고 있음을 알 수 있다.
